
 |
|||
 |
|||
| Load: |

| Store: |
| Multi-cycle control: microprogram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
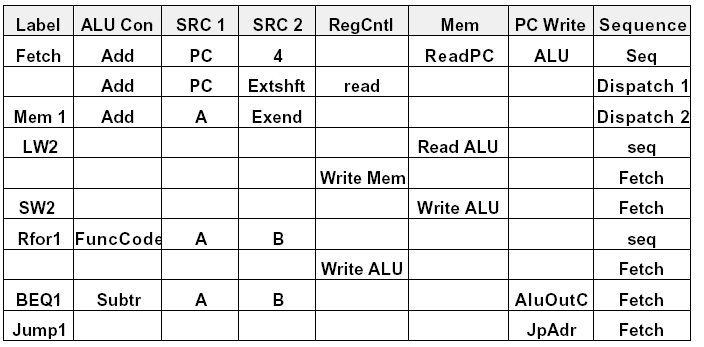
| Complete microprogram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| fetch | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| memory | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R-type | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| branch | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| jump | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fig. 5.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note 10 microinstructions (1 for each state) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sequence: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dispatch1: go to label ending in 1 (Mem1, Rfor1, BEQ1, Jump1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dispatch2: go to label ending in 2 (LW2, SW2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| More complex machines: 100s or 1000s of microinstructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| May also have more temporary registers for holding intermediate results | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Memory access: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||