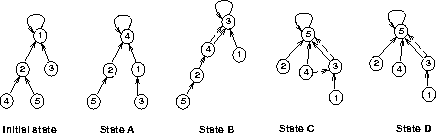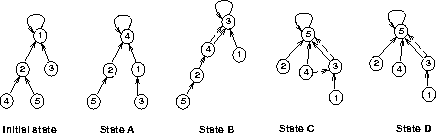CMSC 412 (Fall 94)
Exam 2
Total points 50. Total time 75 mins. Closed book. There are 9 problems
over 5 pages.
1. [6 pts] A process has a page table of 256 entries and
has 3 physical pages allocated to it. The physical pages are initially
empty, and the process generates the following page reference string:
1, 2, 3, 4, 2,
1, 5, 2.
-
a.
-
For LRU replacement, state the number of page faults and the final contents
of the three physical pages.
-
b.
-
For FIFO replacement, state the number of page faults and the final contents
of the three physical pages.
-
c.
-
What is the least number of page faults possible, and why?
2. [6 pts] A demand-paging system has the following utilzations:
20% for the CPU (i.e. CPU busy 20% of time), 98% for the
paging disk, and 5% for other I/O devices.
For each option below, indicate whether (a) it WILL increase CPU utilization;
(b) it MAY increase CPU utilzation; or (c) it will NOT increase CPU
utilization.
-
Install a faster CPU.
-
Install a bigger paging disk.
-
Decrease the degree of multiprogramming.
-
Install more main memory.
-
Install a faster paging disk disk.
-
Add prepaging to the page fetch algorithms.
3. [5 pts] A file of 100 blocks is stored using linked-list
allocation. Assume one file block per disk block. Assume that main memory
contains the disk address of file block 0 and the disk address of the start
of the free list (also organized as a linked list).
-
a.
-
How many disk block accesses are needed to read file block 20?
-
b.
-
How many disk block accesses are needed to add a new file block at the
end?
4. [5 pts] Consider a Unix-style file system using index-nodes
(i-nodes). Assume one file block per disk block. Assume that main memory
contains the disk address of the root's i-node.
-
a.
-
How many disk block accesses are needed to read file block 0 of the file
/usr/adam/hw ?
-
b.
-
Suppose that /u/sue is a symbolic link to /usr/adam/hw.
How many disk block accesses are needed to read file block 0 of the file
(pointed to by) /u/sue ?
5. [5 pts] Consider a distributed shared memory system that
uses the write-invalidate protocol. Suppose that cpu 1 periodically writes
to a certain virtual page, and between two successive writes, M
other cpus read the page. For this page, how many messages are sent system-wide
between every two writes. Assume point-to-point communication, i.e. if
a message is to be delivered to multiple cpus, it has to be sent separately
to each one.
6. [6 pts] Consider demand-paging with virtual address
space of 1 M words, physical memory of 256 K words, page size of 1 K words,
FIFO page replacement, and an associative map of 4 entries using LRU replacement.
-
a.
-
Give the organization (format, field labels, widths) of the following:
virtual address, physical address, page map
table, associative map.
-
b.
-
Assume the CPU starts executing a process whose virtual page i is
mapped to physical page i+2. Assume the associative map is initially
empty and the process generates the following sequence of addresses (in
HEX):
0x 023FE
Ox 031FD
Ox 022A0
0x 01570
0x 02F01
0x 01F00
Describe the contents of the associative map at the end.
7. [7 pts] A demand-paging system executes N user processes
using a non-premptive FIFO discipline for sharing the cpu. A user process
gives up the cpu if and only if it has a page fault. There is a disk-io
process that handles disk io.
A user process never terminates. Whenever a user process is started/resumed,
it executes for X msec and then has a page fault. The page fault
handler takes Y msec to execute; it sends the appropriate io request
to the disk-io process. The disk-io process wakes up the user process when
its io completes. Assume that the disk-io process uses negligible cpu time,
and that pages never have to be written back to disk.
Let T denote the time between successive page faults for any
particular user process (say, user process 1).
-
a.
-
Assume that every io request takes Z msec to complete starting
from when the request is sent to disk-io, no matter how many other io requests
are currently being handled. Let Z > 100 X + 100 Y.
Obtain T and the cpu utilization (i.e. fraction of time cpu is
executing) for N = 1 and for N = 10.
-
b.
-
Now assume that io requests are serviced in FIFO manner; i.e. the
disk starts on a request only after it completes serving the previous request.
The disk takes Z msec to serve the request, where Z > 100
X + 100 Y.
Obtain T and the cpu utilization for N = 1 and for N
= 10.
-
c.
-
Which is more realistic, the assumption in part a or the assumption in
part b. Why?
8. [5 pts] A distributed shared memory system uses the path
compression algorithm to share a virtual page among cpus 1, 2, 3, 4, and
5. Initially, cpu 1 owns the page, and the last pointers are as
shown below. Then the following sequence of events happens:
-
4 sends request for page (i.e. to become owner).
-
Request arrives at its final destination.
-
1 sends page.
-
4 receives page.
*** STATE A ***.
-
4 starts accessing page.
-
3 sends request for page.
-
Request arrives at its final destination (4 still accessing page).
*** STATE B ***.
-
6 sends request for page.
-
Request arrives at its final destination (4 still accessing page).
*** STATE C ***.
-
4 finishes accessing page.
-
4 sends page
-
Page is received.
*** STATE D ***.
For each of the places marked above, draw the graph of the last
and next pointers (use dotted arc for next pointers).
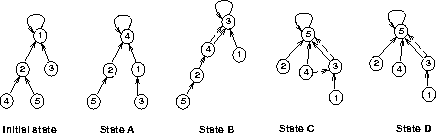
Initial state State A State B State C State
D
9. [5 pts] The path-compression algorithm uses the next
pointers to maintain a distributed queue of waiting cpus (e.g. if cpu 1
is accessing the page and receives a request by cpu 3, it sets its next
to 3).
BRIEFLY explain how to modify the algorithm so that queues of waiting
cpus are maintained within nodes; that is, if cpu 1 is accessing the page
and receives a request by cpu 3 and then a request by cpu 4, then cpu 1
should have a queue containing the ids 3 and 4.
A. Udaya Shankar
Thu Nov 19 12:54:32 EST 1998